

The ASTM D3985 Standard test measurement system is widely used for measuring the oxygen vapour permeability of a plastic film or sheet. It is based on using a coulometric oxygen sensor and can produce extremely accurate results. The same technique is often used for laminates, coextrusions, or plastic-coated papers or even fabrics.
This standard only relates to oxygen permeability testing under steady-state conditions where the Relative Humidity (RH) is under 1%. (See below for conditions where RH is higher or variable)
The ASTM D3985 test method is for the determination of :
1. Oxygen gas transmission rate (OTR)
2. The permanence of the film to oxygen gas (PO2
3. The oxygen permeability coefficient (P′O2) in the case of homogeneous materials
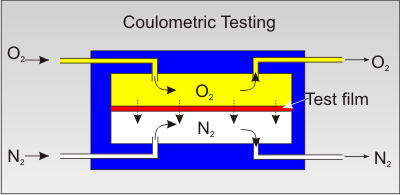 This test method is not the only method for measuring OTR. Other methods are available using other oxygen sensors and procedures. The choice of a test method can be based on the application and other practical concerns.
This test method is not the only method for measuring OTR. Other methods are available using other oxygen sensors and procedures. The choice of a test method can be based on the application and other practical concerns.
The ASTM D3985 Testing Method:
Under the ASTM D3958 testing procedure a plastic sheet specimen is mounted between two chambers as a sealed semi-barrier between them. The upper chamber contains oxygen while the lower is slowly purged with a stream of nitrogen as a carrier gas. The process must take place under steady state conditions and with RH < 1%.
As the oxygen permeates through the film and into the nitrogen carrier gas, it is carried to the coulometric sensor where it creates an electrical current. The magnitude of this current is absolutely proportional the amount of oxygen received by the detector per unit time. This is a direct consequence of Faraday’s Law.
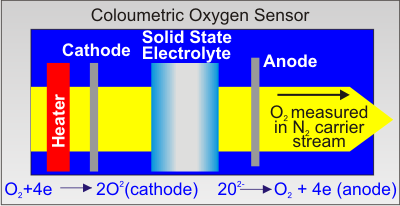
The oxygen flows from one chamber to the other because its partial pressure (concentration) in the upper chamber it greater than is in the lower chamber. This difference is maintained by the plastic barrier so that the flow of oxygen through the barrier gives a direct measurement of the plastic's oxygen vapour permeability.
The oxygen permeability of most plastic films shows considerable variation under humid conditions (i.e. when RH varies). In these cases a different standard method (ASTM F 1927) should be used. Measuring oxygen vapour permeability under humid conditions requires very strict environmental control. Such control is an optional feature on all Versaperm instrumental vapour permeability measurement equipment.
At Versaperm we are not tied to any specific sensor types or manufacturer and so we can always select exactly the right sensor for an application. Versaperm is a world technology leader in the measurement of gas permeability. We offer not only instruments but also comprehensive testing and consultancy services.
Click here for details of the Versaperm Range of Mk VI Permeability Meters.