Helium Vapour Permeability
 Helium permeability measurements are widely used across multiple scientific and industrial sectors, mainly because helium is:
Helium permeability measurements are widely used across multiple scientific and industrial sectors, mainly because helium is:
- The smallest and lightest noble gas, making it ideal for detecting minute leaks
- Chemically inert and non-reactive, so it doesn’t alter the materials being tested
- A proxy for measuring general gas barrier performance due to its high diffusivity
Here are the main uses of helium gas permeability measurements:
1. Leak Detection and Seal Integrity
- Vacuum systems, medical devices, aerospace components and semiconductor manufacturing often rely on helium for ultra-sensitive leak testing
- If a material is permeable to helium, it may also allow other critical gases to leak or contaminate
2. Barrier Material Testing
- Used to assess films, coatings, foils and packaging materials in pharmaceuticals, food and electronics
- High helium permeability in barrier films can indicate poor performance in protecting against gas exchange, moisture ingress, or volatile loss
 3. Aerospace and Defence Applications
3. Aerospace and Defence Applications
- Aerospace systems require hermetically sealed environments, especially in fuel systems and avionics
- Helium testing helps ensure integrity under vacuum or high-pressure differential conditions
4. Cryogenic and Superconducting Systems
- Helium is used as a cryogen (especially in its liquid state for superconducting magnets)
- Containment systems and insulation materials must be helium-tight, especially in MRI machines, particle accelerators, or fusion reactors
5. Membrane and Porosity Characterisation
- Porous materials, like those used in filtration, catalysis, or hydrogen separation, are characterised using helium permeability to understand pore size and structure
- Helium's small atomic size makes it useful for testing micro- and nano-porous materials
6. Nuclear and High-Energy Physics
- In fusion reactors, like ITER, helium (and tritium) permeability is critical for containment materials and reactor safety
- Also used in radioactive waste containment, where long-term barrier performance must be measured
Measurement and Instrumentation
- Instruments such as Versaperm’s vapour permeability meters (including those with mass spectrometry detectors) are well suited for helium permeability testing.
Summary of Helium Permeability Applications:
Industry |
Use Case |
Packaging |
Barrier performance testing |
Aerospace |
Leak integrity in pressurised and vacuum systems |
Cryogenics |
Containment of helium in superconducting and cooling systems |
Nuclear/Fusion |
Testing permeability of reactor walls and containment materials |
Electronics |
Encapsulation testing for semiconductors and sensors |
Material Science |
Pore size characterisation and gas diffusion research |
APPLICATIONS
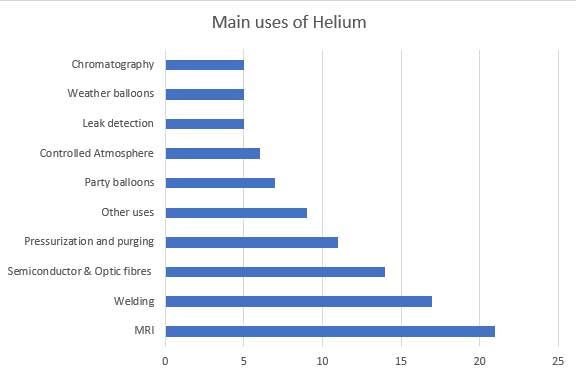
It's crucial in medical imaging (MRI), scientific research (cryogenics) and various industrial processes due to its unique properties. Specifically, it's used as a coolant, in welding and in the manufacturing of semiconductors and fibre optics.
Here's a more detailed look at helium's applications:
Medical Applications:
 MRI:
MRI:
Liquid helium is used to cool the superconducting magnets in MRI machines, enabling high-resolution imaging for diagnostics.
Helium-oxygen (heliox) mixtures can help patients with respiratory conditions like asthma and emphysema by reducing airflow resistance.
Scientific Research:
Helium is essential for creating and maintaining extremely low temperatures needed in various research fields, including particle physics and materials science.
Helium cools superconducting magnets used in particle accelerators and NMR systems.
The unique behaviour of liquid helium (helium I and helium II) is studied to understand quantum mechanics and superfluidity.
Industrial Applications:
Helium provides an inert shield gas for arc welding, preventing oxidation and contamination.
Helium is used in the manufacturing of semiconductors, including as a cooling agent and in processes like plasma etching.
Helium is used to prevent bubbles in the manufacturing of fibre optic cables.
Helium's small atomic size makes it effective for detecting leaks in various systems.
Helium is used to cool various industrial processes and equipment, including in the production of titanium and zirconium.
Helium acts as a coolant in some nuclear reactors, as it does not become radioactive.
 Other Applications:
Other Applications:
- Balloons and Airships: Helium is used to lift balloons and airships due to its low density
- Space Exploration: NASA uses helium in rockets for pressurizing fuel tanks and cooling systems
- Barcode Scanners: Helium-neon lasers are used in barcode scanners
- Hard Drives: Helium-filled hard drives are becoming increasingly common, offering advantages in speed, size and energy efficiency
STANDARDS
Here's a list of key standards related to helium permeability and helium leak testing, covering both material permeability testing and system-level leak detection. These standards are used across sectors such as aerospace, medical devices, packaging and high-vacuum applications.
Helium Permeability and Transmission Standards
1. ASTM D1434
- Title: Standard Test Method for Determining Gas Permeability Characteristics of Plastic Film and Sheeting
- Use: General-purpose method for measuring the rate of helium and other gases through flexible barrier materials
- Industry: Packaging, electronics, research
2. ISO 15105-1
- Title: Plastics – Film and sheeting – Determination of gas transmission rate – Part 1: Differential-pressure method
- Use: Similar to ASTM D1434; used for comparative measurement of gas permeability, including helium
- Industry: Packaging, polymers
3. ISO 15105-2
- Title: Plastics – Film and sheeting – Determination of gas transmission rate – Part 2: Equal-pressure method
- Use: Another standard method applicable to helium permeability testing
Helium Leak Detection Standards
4. ASTM E499 / E499M
- Title: Standard Practice for Leaks Using the Mass Spectrometer Leak Detector in the Tracer Probe Technique
- Use: Detection of leaks using helium as a tracer gas; widely used in aerospace, automotive and medical devices
5. ASTM E498 / E498M
- Title: Standard Practice for Mass Spectrometer Leak Testing of Brazed Joint Assemblies
- Use: Helium leak testing in vacuum-tight assemblies (e.g., tubes, fittings, seals)
6. ASTM F2391
- Title: Standard Test Method for Measuring Package and Seal Integrity Using Helium as a Tracer Gas
- Use: Common in the pharmaceutical industry; ensures package integrity using helium
7. ISO 20484
- Title: Fine Ceramics (Advanced Ceramics, Advanced Technical Ceramics) – Test Method for Gas Permeability
- Use: Includes helium; used for advanced barrier materials
8. ISO 14687
- Title: Hydrogen fuel – Product specification
- Use: Specifies limits on helium and other contaminants in hydrogen fuel, relevant for systems where helium permeation or leakage may influence purity
Sector-Specific and Supplementary Standards
- MIL-STD-883: Test methods for microelectronics (includes helium leak testing for hermeticity)
- IEC 60068-2-17: Test methods for hermetic seals in electronics (includes tracer gas methods)
- EN 13185 / 13192: European standards for non-destructive leak testing using tracer gases


 Helium permeability measurements are widely used across multiple scientific and industrial sectors, mainly because helium is:
Helium permeability measurements are widely used across multiple scientific and industrial sectors, mainly because helium is: 3. Aerospace and Defence Applications
3. Aerospace and Defence Applications MRI:
MRI: Other Applications:
Other Applications: